Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Solution: Using Sliding Window
We can use variable sized Sliding Window Pattern to solve this problem.
Step 1
Assuming the targetSum = 7.
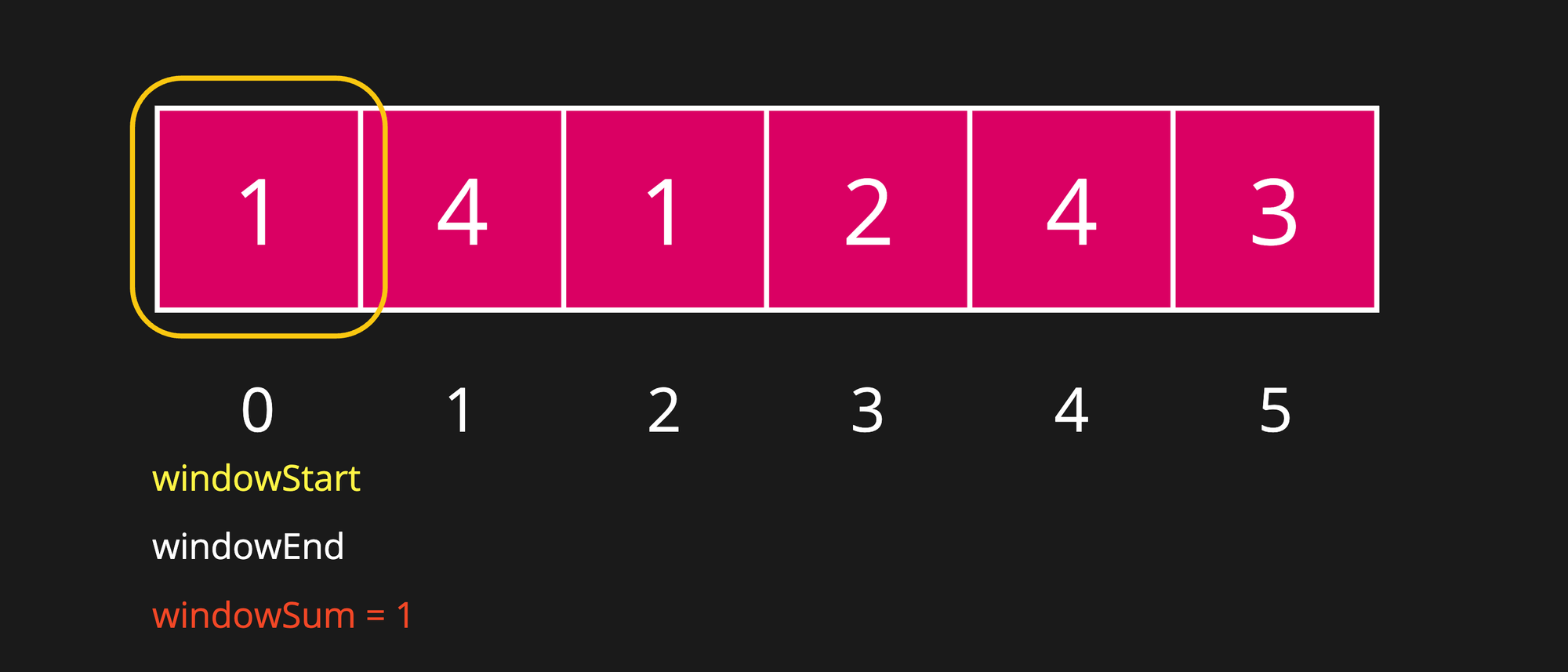
windowSum is still less than targetSum i.e. 1 < 7, continue to expand the window.
Step 2
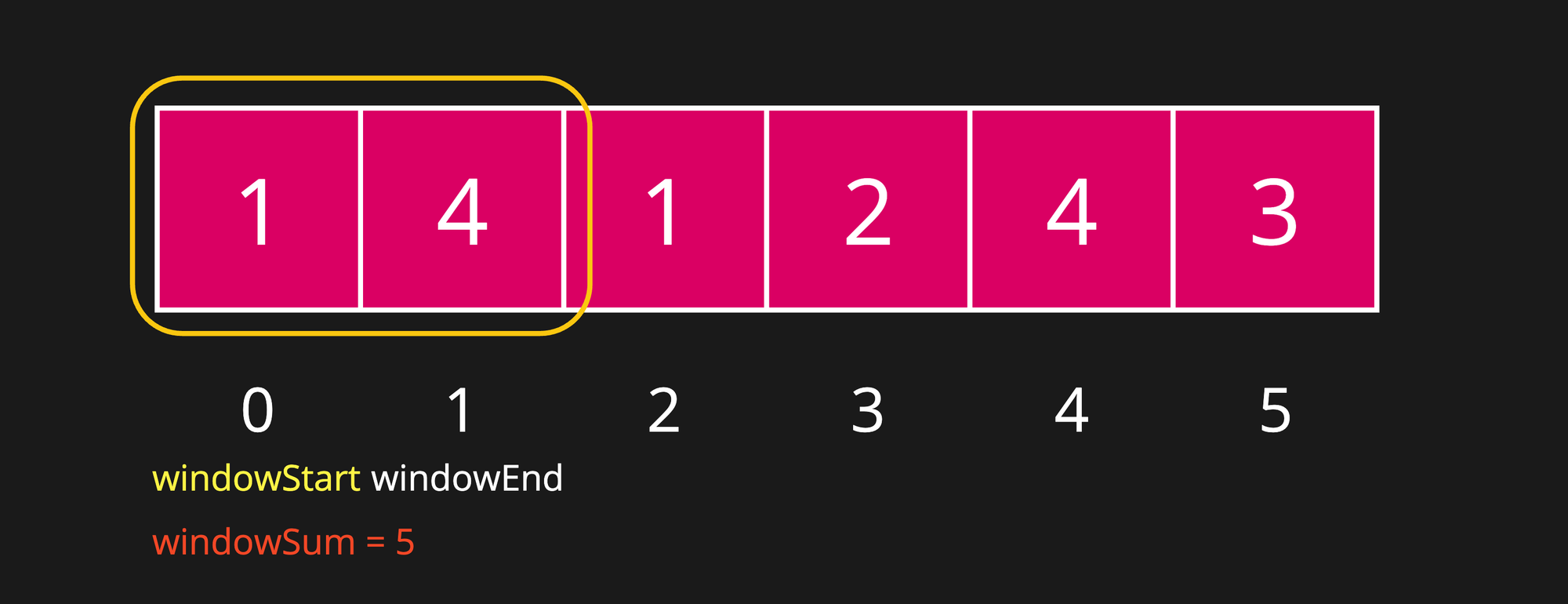
windowSum is still less than targetSum i.e. 5 < 7, continue to expand the window.
Step 3
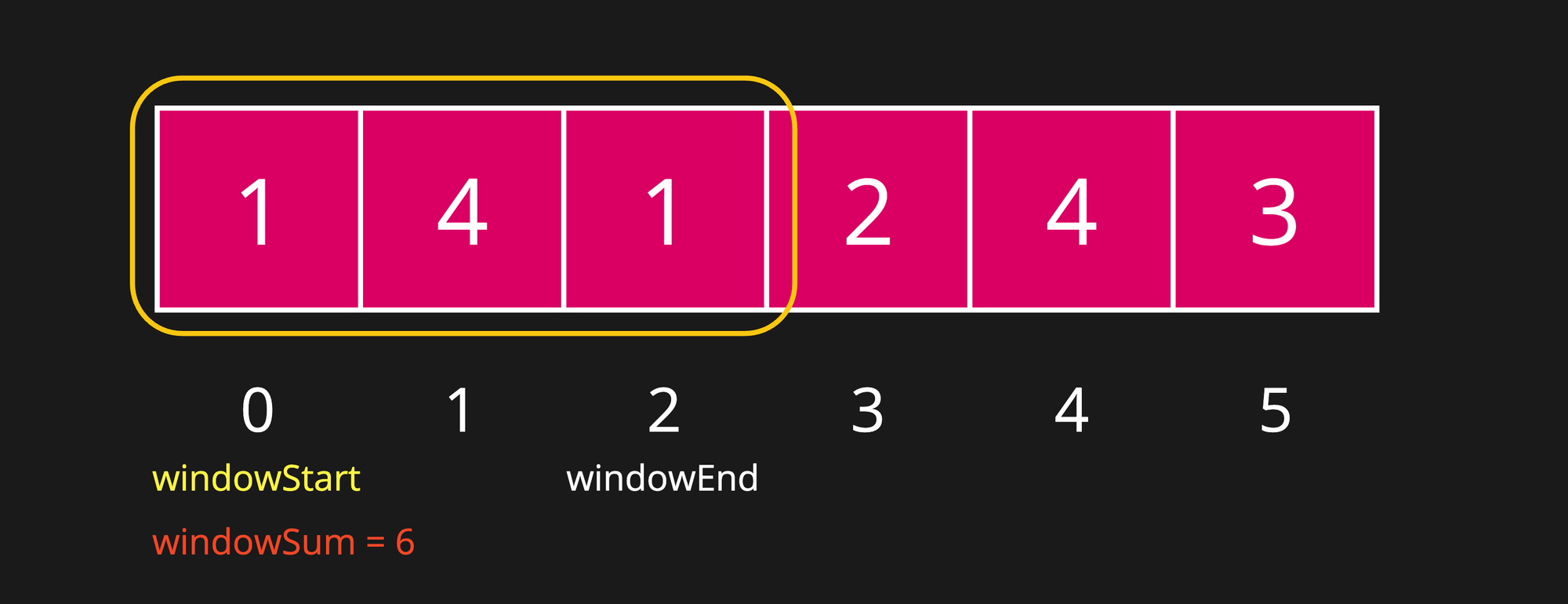
windowSum is still less than targetSum i.e. 6 < 7, continue to expand the window.
Step 4
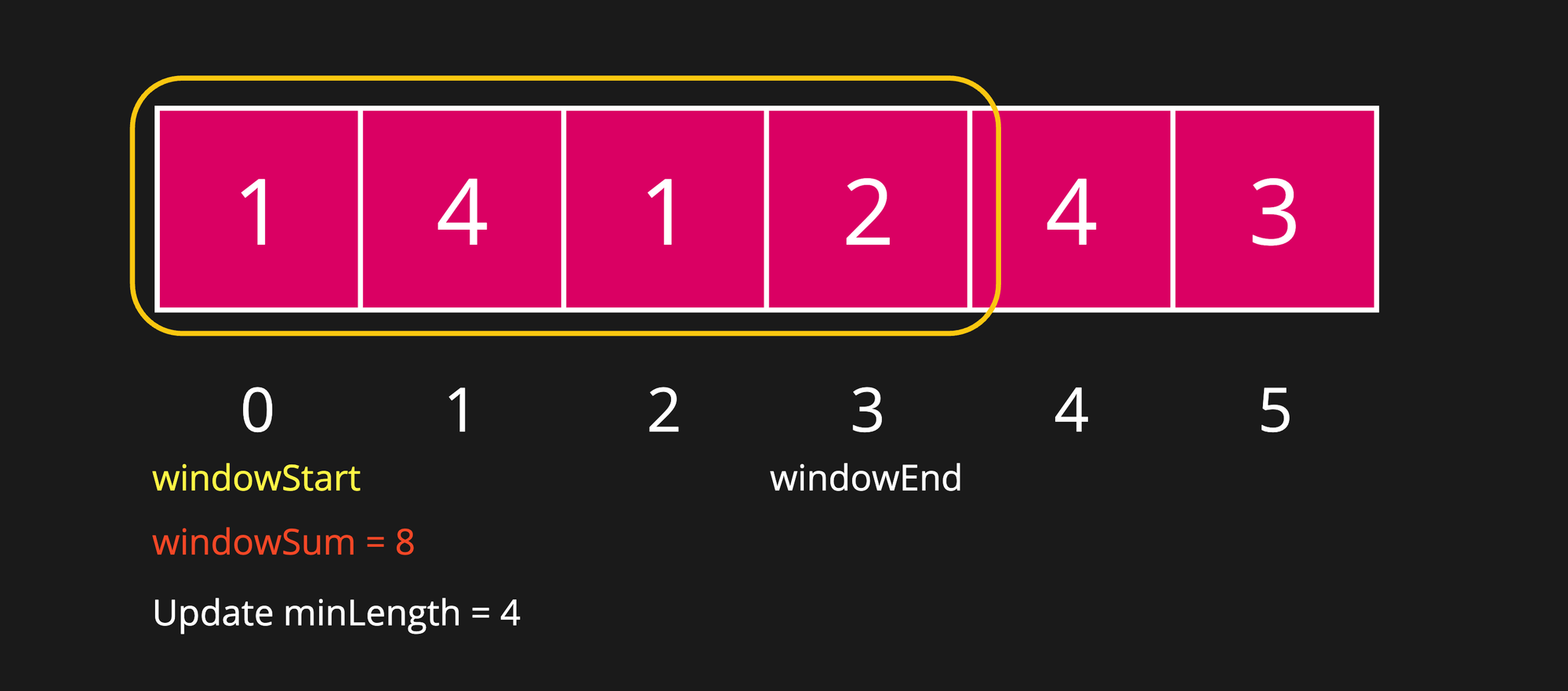
windowSum is now greater than or equal to targetSum i.e. 8 >= 7. At this point, we should store this window size as one of the answers.
Now, we should shrinking this window and look if any smaller window is present.
Step 5
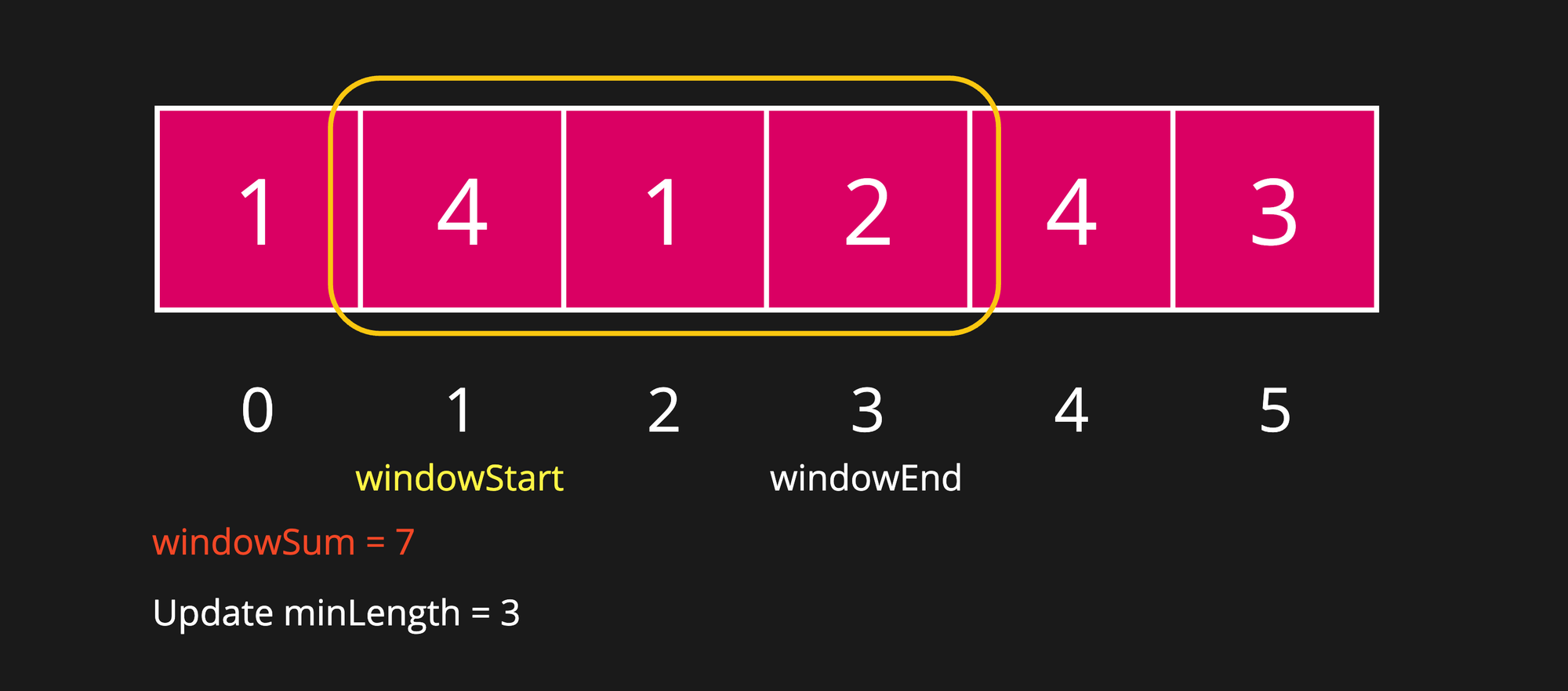
After shrinking the window, the windowSum has become 7, which is still greater than or equal to targetSum. Hence, we have found a better answer. Therefore, update minLength to current window size which is 3.
Step 6
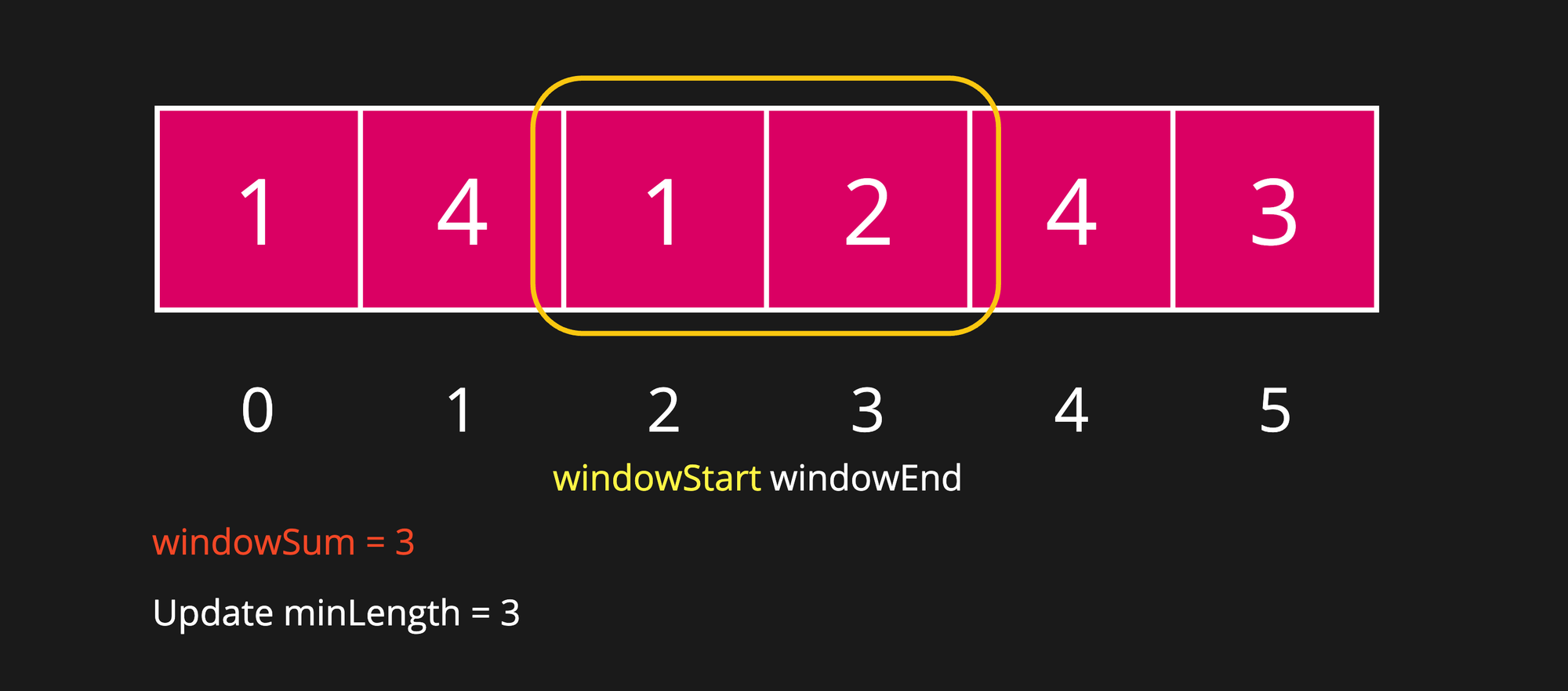
After shrinking the window one more time, we have got windowSum smaller to targetSum which means an invalid window. Hence, now we would start expanding the window again to find a better answer.
Step 7
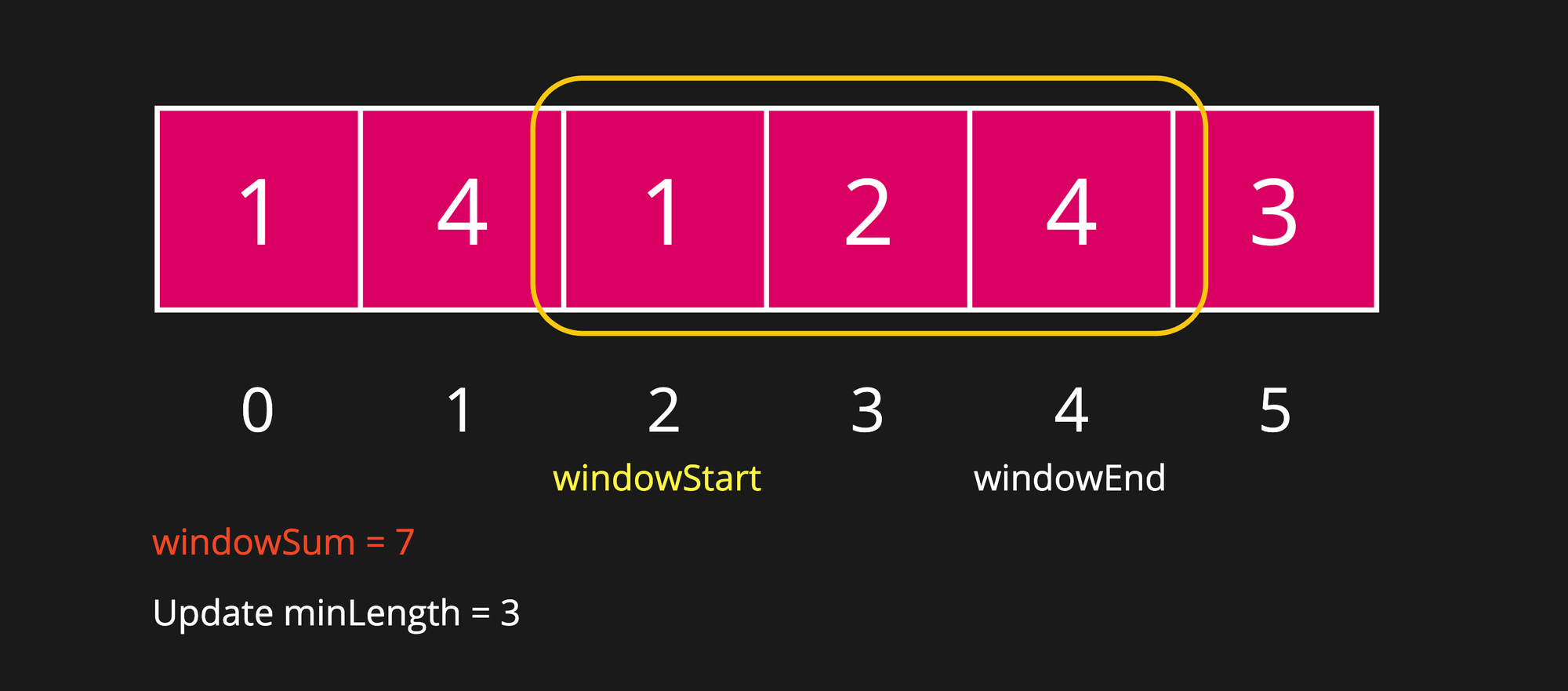
After expanding window, we have again got windowSum greater than or equal to targetSum. Let's update the minLength. But the minLength is already 3 so it won't get updated.
As a next step, we will try to shrink the window again from the left side in order to find the minLength.
Step 8
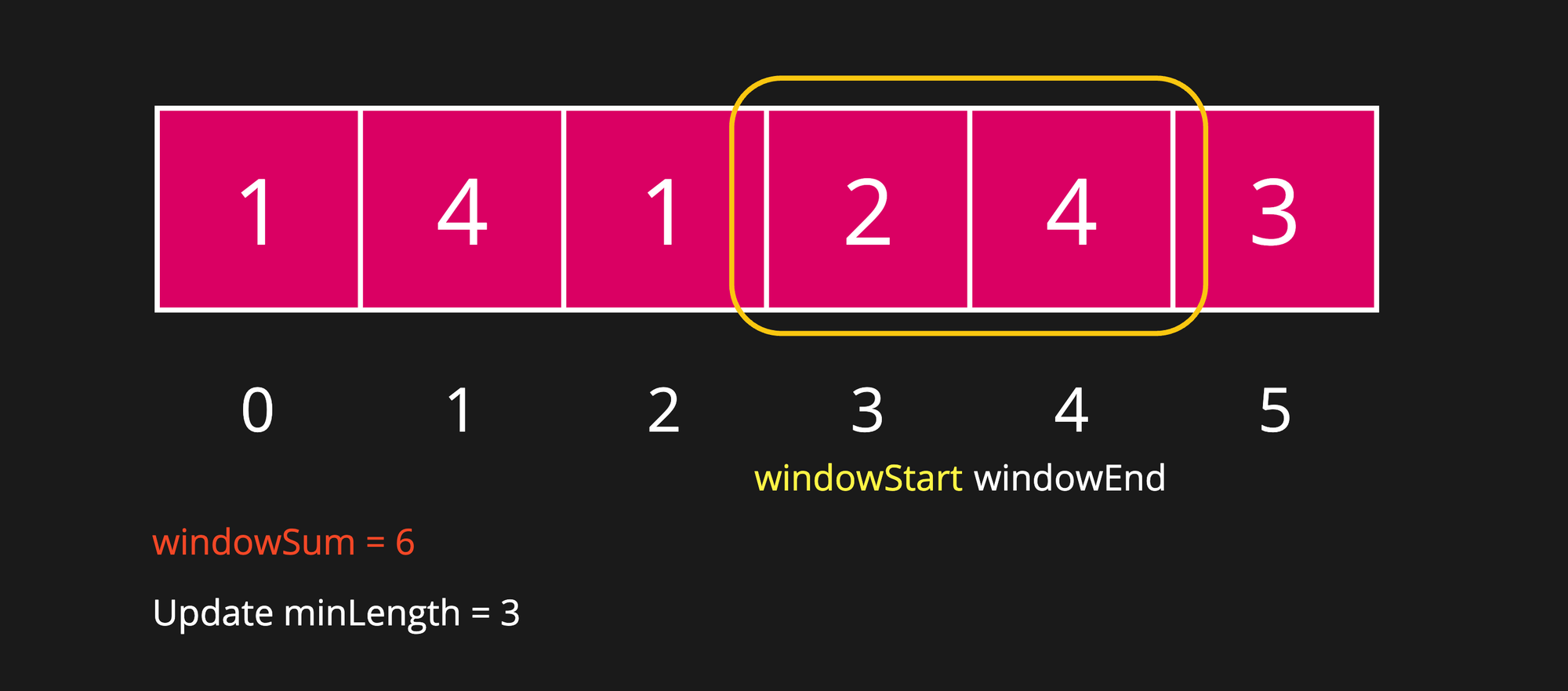
After shrinking the window, we have got an invalid window again. So, let's try expanding it again.
Step 9
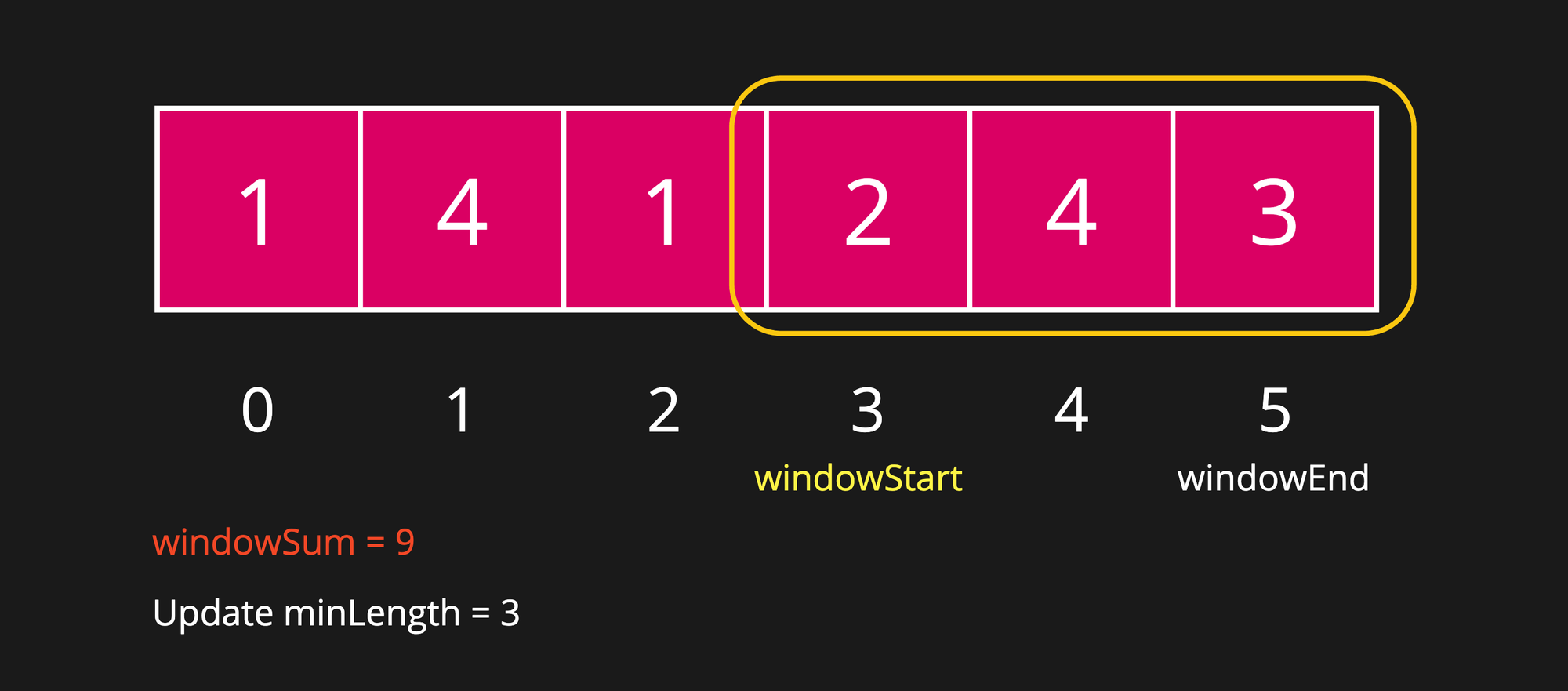
After expanding window, we have again got windowSum greater than or equal to targetSum. Let's update the minLength. But the minLength is already 3 so it won't get updated.
As a next step, we will try to shrink the window again from the left side in order to find the minLength.
Step 10
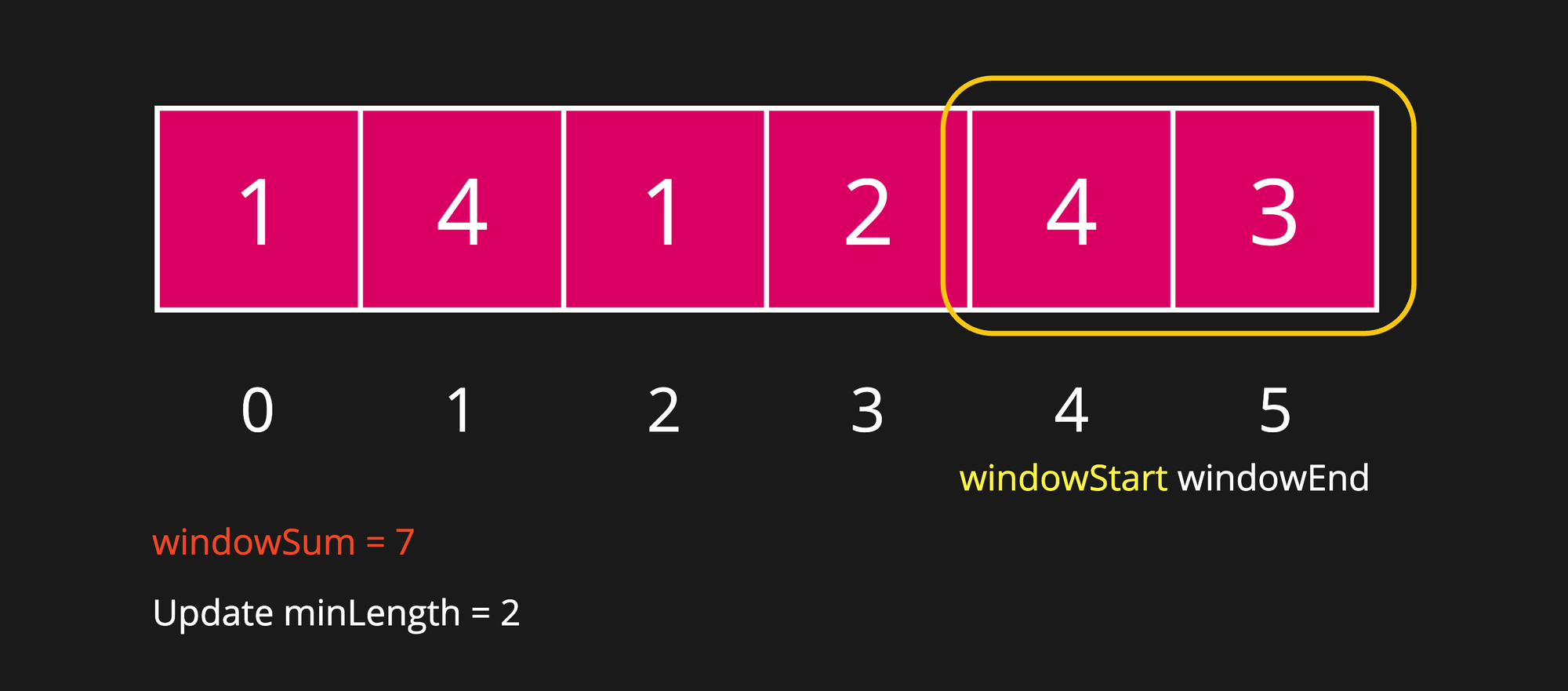
Even after shrinking the window, the windowSum has become 7, which is still greater than or equal to targetSum. Hence, we have found a better answer. Therefore, update minLength to current window size which is 2.
As a next step, we will try to shrink the window again from the left side in order to find the minLength.
Step 11
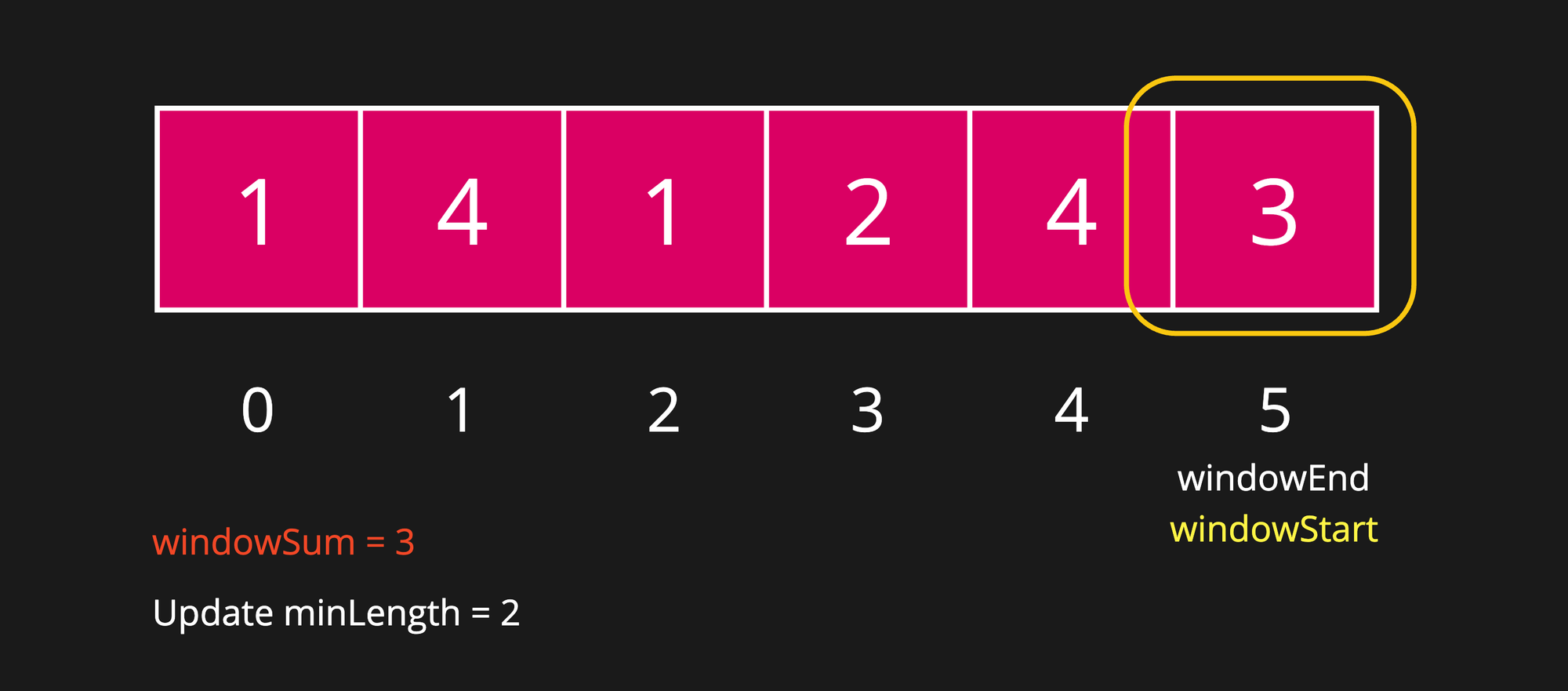
After shrinking the window, we have got an invalid window again. So, let's try expanding it again.
Step 12
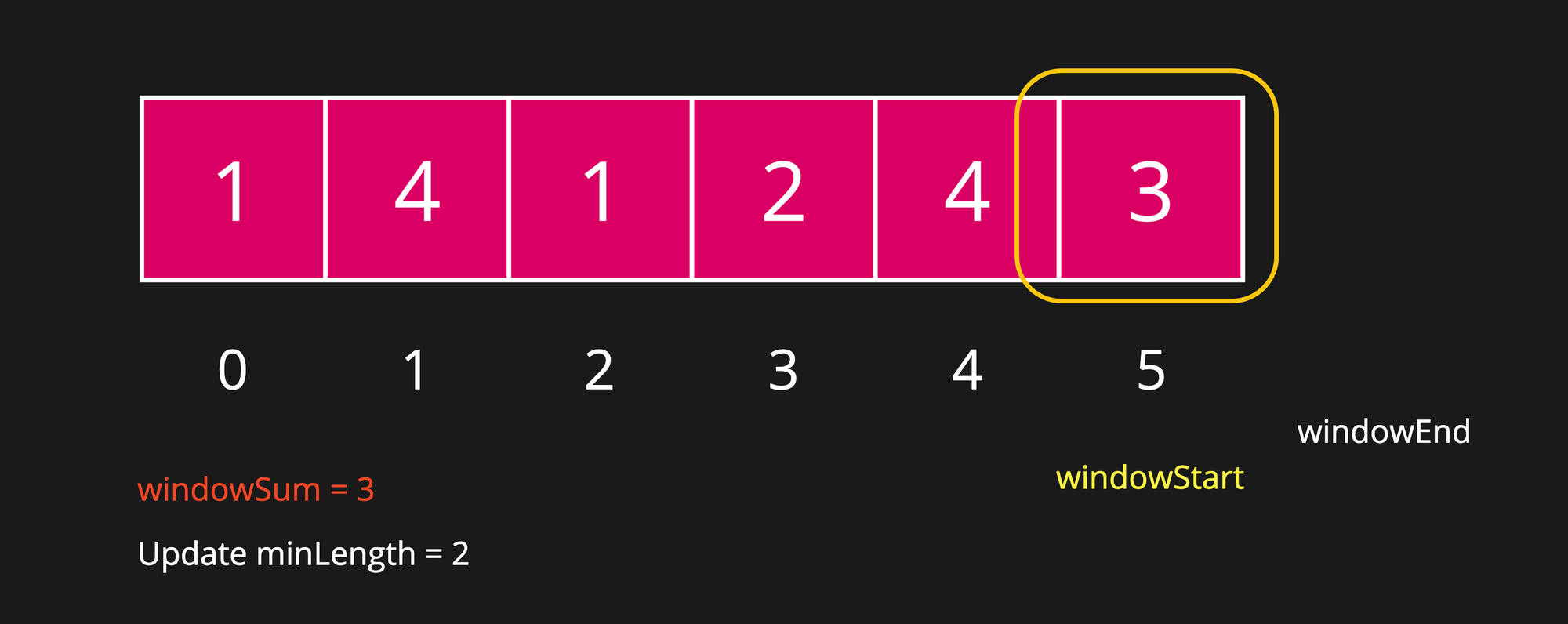
The loop will be terminated here, hence return minLength.
Let's look at the code now.
Java Code
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int windowStart = 0;
int windowSum = 0;
int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int windowEnd = 0; windowEnd < nums.length; windowEnd++) {
windowSum += nums[windowEnd];
while(windowSum >= target) {
minLength = Math.min(minLength, windowEnd - windowStart + 1);
windowSum -= nums[windowStart];
windowStart += 1;
}
}
return (minLength == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? 0 : minLength;
}
}
C++ Code
class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int target, vector<int>& nums) {
int windowStart = 0;
int windowSum = 0;
int minLength = INT_MAX;
for(int windowEnd = 0; windowEnd < nums.size(); windowEnd++) {
windowSum += nums[windowEnd];
while(windowSum >= target) {
minLength = min(minLength, windowEnd - windowStart + 1);
windowSum -= nums[windowStart];
windowStart += 1;
}
}
if(minLength == INT_MAX) return 0;
else return minLength;
}
};
Python Code
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, target: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
windowStart = 0
windowSum = 0
minLength = math.inf
for windowEnd in range(len(nums)):
windowSum += nums[windowEnd]
while(windowSum >= target):
minLength = min(minLength, windowEnd - windowStart + 1)
windowSum -= nums[windowStart]
windowStart += 1
return 0 if minLength == math.inf else minLength
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the size of the array nums.
Space Complexity: O(1)