Introduction to Sliding Window Pattern
Problem Statement
Given an array of integer nums, check if there is a subarray of size K whose sum is equal to the target.
Example
Input:
nums = [9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2]
K = 4
target = 26
Output: true
Explanation: There is a subarray of size 4 [8, 5, 6, 7] whose sum is equal to 26.
Solution: Brute Force
Java Code
class Solution {
private static boolean subarrayExists(int[] nums, int k, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < n - k + 1; i++) {
int subarraySum = 0;
for(int j = i; j < i + k; j++) {
subarraySum += nums[j];
}
if(subarraySum == target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[]{9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2};
int k = 4;
int target = 26;
System.out.println(subarrayExists(nums, k, target));
}
}
C++ Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
static bool subarrayExists(vector<int> nums, int k, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= n - k; i++) {
int subarraySum = 0;
for (int j = i; j < i + k; j++) {
subarraySum += nums[j];
}
if (subarraySum == target) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2};
int k = 4;
int target = 26;
cout << (Solution::subarrayExists(nums, k, target) ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
}
Python Code
class Solution:
def subarrayExists(self, nums, k, target):
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n - k + 1):
subarray_sum = 0
for j in range(i, i + k):
subarray_sum += nums[j]
if subarray_sum == target:
return True
return False
nums = [9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2]
k = 4
target = 26
print(Solution().subarrayExists(nums, k, target))
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N * K), where N is the size of the array nums, and K is the size of the subarray.
Space Complexity: O(1)
Solution 2: Using Sliding Window
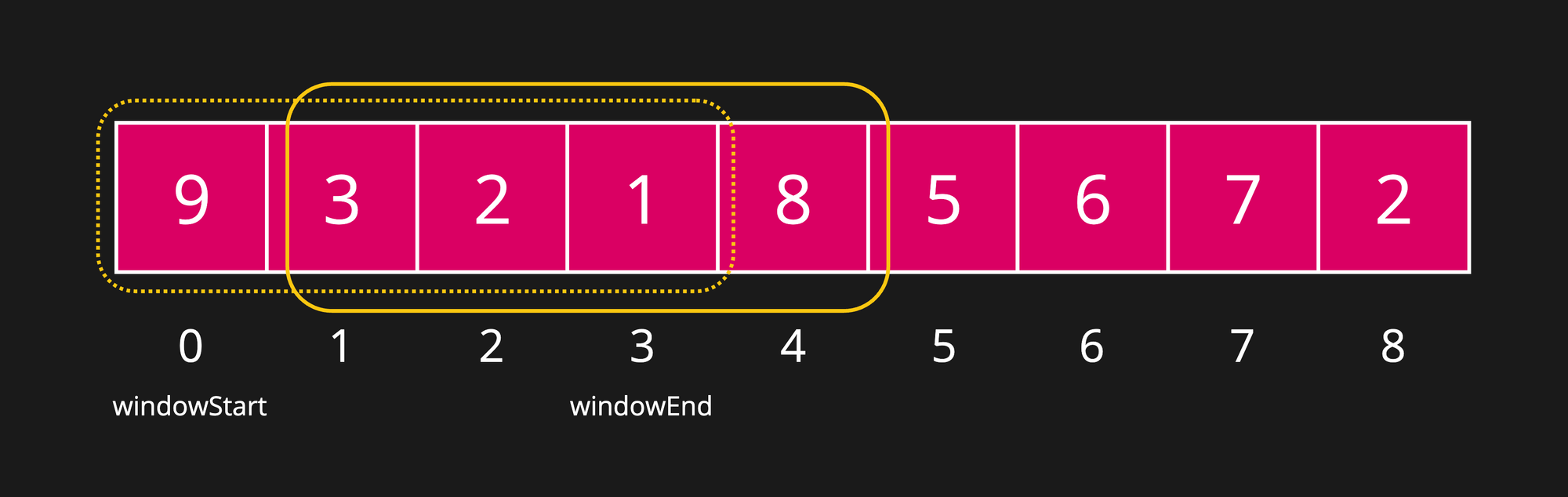
Java Code
class Solution {
private static boolean subarrayExists(int[] nums, int k, int target) {
int windowStart = 0;
int windowSum = 0;
for(int windowEnd = 0; windowEnd < n; windowEnd++) {
windowSum += nums[windowEnd];
if(windowEnd >= (k - 1)) {
if(windowSum == target) {
return true;
}
windowSum -= nums[windowStart];
windowStart += 1;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = new int[]{9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2};
int k = 4;
int target = 26;
System.out.println(subarrayExists(nums, k, target));
}
}
C++ Code
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
static bool subarrayExists(vector<int>& nums, int k, int target) {
int windowStart = 0, windowSum = 0;
int n = nums.size();
for (int windowEnd = 0; windowEnd < n; windowEnd++) {
windowSum += nums[windowEnd];
if (windowEnd >= k - 1) {
if (windowSum == target) {
return true;
}
windowSum -= nums[windowStart];
windowStart++;
}
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2};
int k = 4;
int target = 26;
cout << (Solution::subarrayExists(nums, k, target) ? "True" : "False") << endl;
return 0;
}
Python Code
class Solution:
def subarrayExists(self, nums, k, target):
window_start = 0
window_sum = 0
n = len(nums)
for window_end in range(n):
window_sum += nums[window_end]
if window_end >= k - 1:
if window_sum == target:
return True
window_sum -= nums[window_start]
window_start += 1
return False
nums = [9, 3, 2, 1, 8, 5, 6, 7, 2]
k = 4
target = 26
print(Solution().subarrayExists(nums, k, target))
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the size of the array nums.
Space Complexity: O(1)