Introduction to Linked Lists
A linked list is a data structure used for storing collections of data. A linked list has the following properties:
- Successive elements are connected by pointers.
- The last element points to
null. - Can grow or shrink in size during execution of a program.
- Can be made just as long as required (until system memory exhausts).
- Does not waste memory space (but takes some extra memory for storing pointers). It allocates memory as list grows.
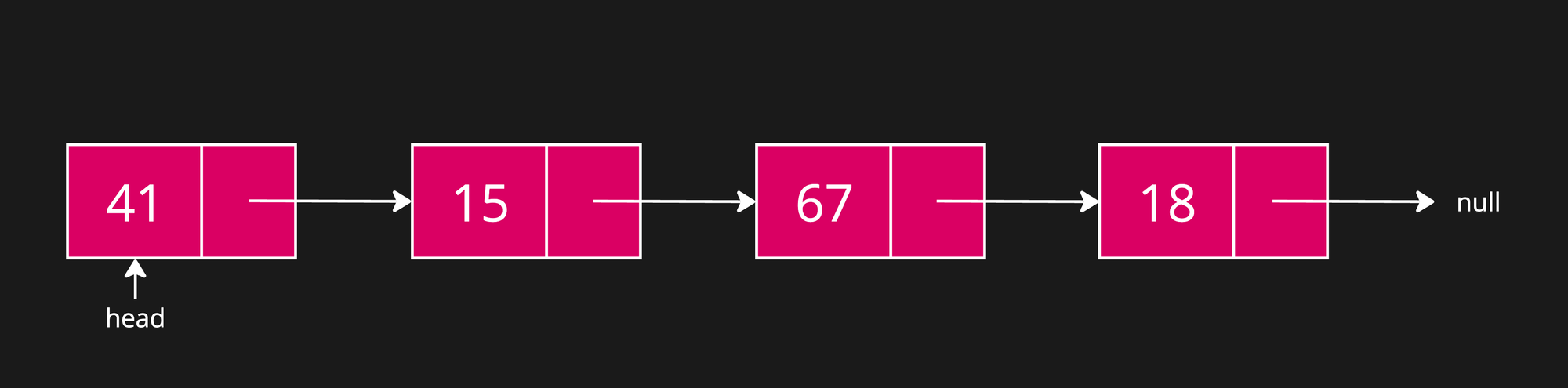
Linked Lists are comprises of Nodes.
What is a Node?
A Node in a Linked List is a fundamental building block that holds two pieces of information:
- data – the actual value or information you want to store (like an integer, string, object, etc.).
- next (Pointer or Reference) – a link to the next node in the list.
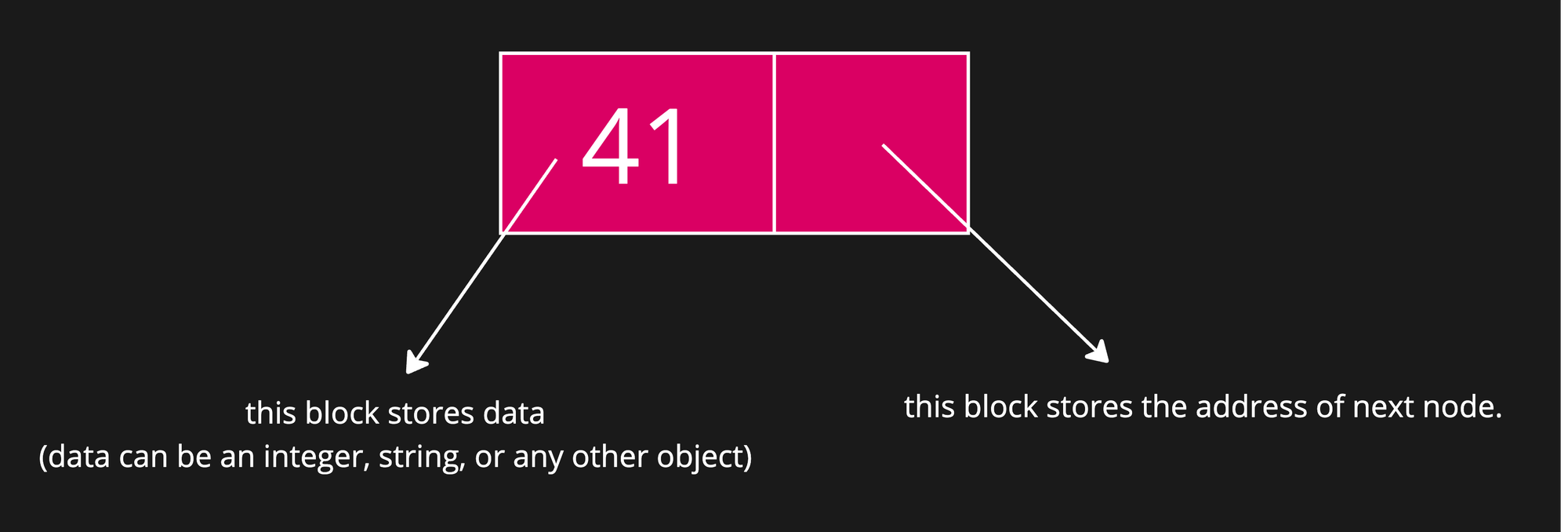
How do we represent a Node in Java?
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Create a linked list using nodes
Step 1: Create individual nodes
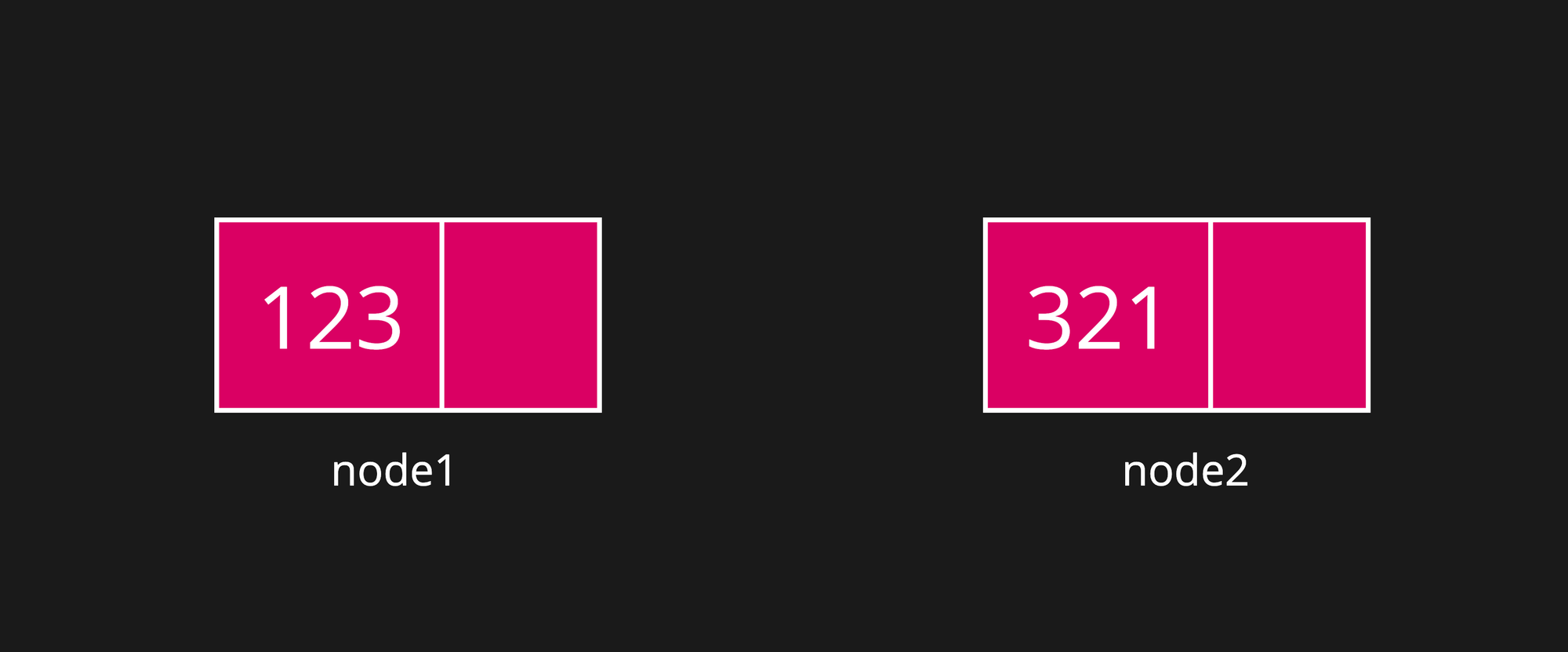
Node node1 = new Node(123);
Node node2 = new Node(321);
Step 2: Link the first node to the second
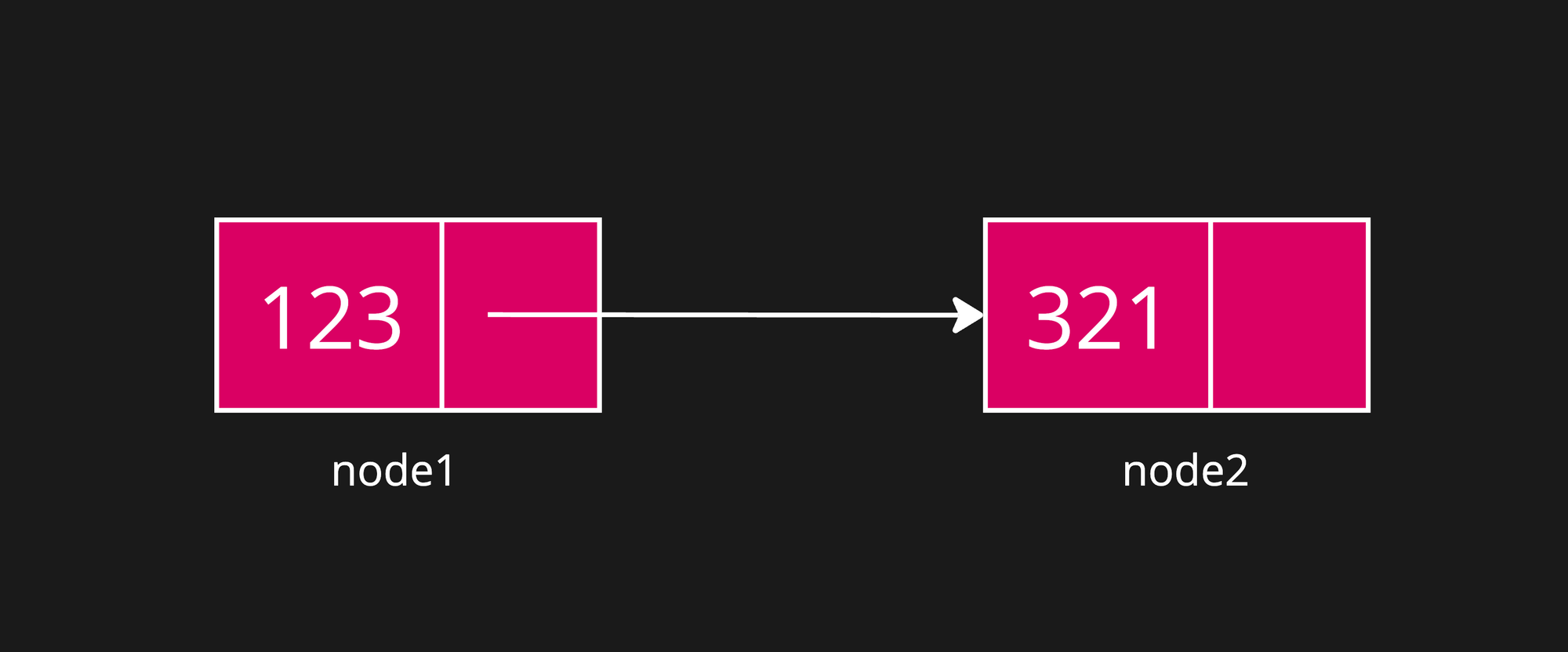
node1.next = node2;
Step 3: Access linked nodes
System.out.println(node1.data); // 123
System.out.println(node2.data); // 321
System.out.println(node1.next.data); // 321
Complete Java Code
Create a class BasicNodeStructure.java.
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class BasicNodeStructure {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node1 = new Node(123);
Node node2 = new Node(321);
node1.next = node2;
System.out.println(node1.data);
System.out.println(node2.data);
System.out.println(node1.next.data);
}
}
Compile and run by running following two commands.
javac BasicNodeStructure.java
java BasicNodeStructure
Output
123
321
321