Surrounded Regions
Problem Statement
Given an m x n matrix board containing 'X' and 'O', capture all regions that are 4-directionally surrounded by 'X'.
A region is captured by flipping all 'O's into 'X's in that surrounded region.
Example 1
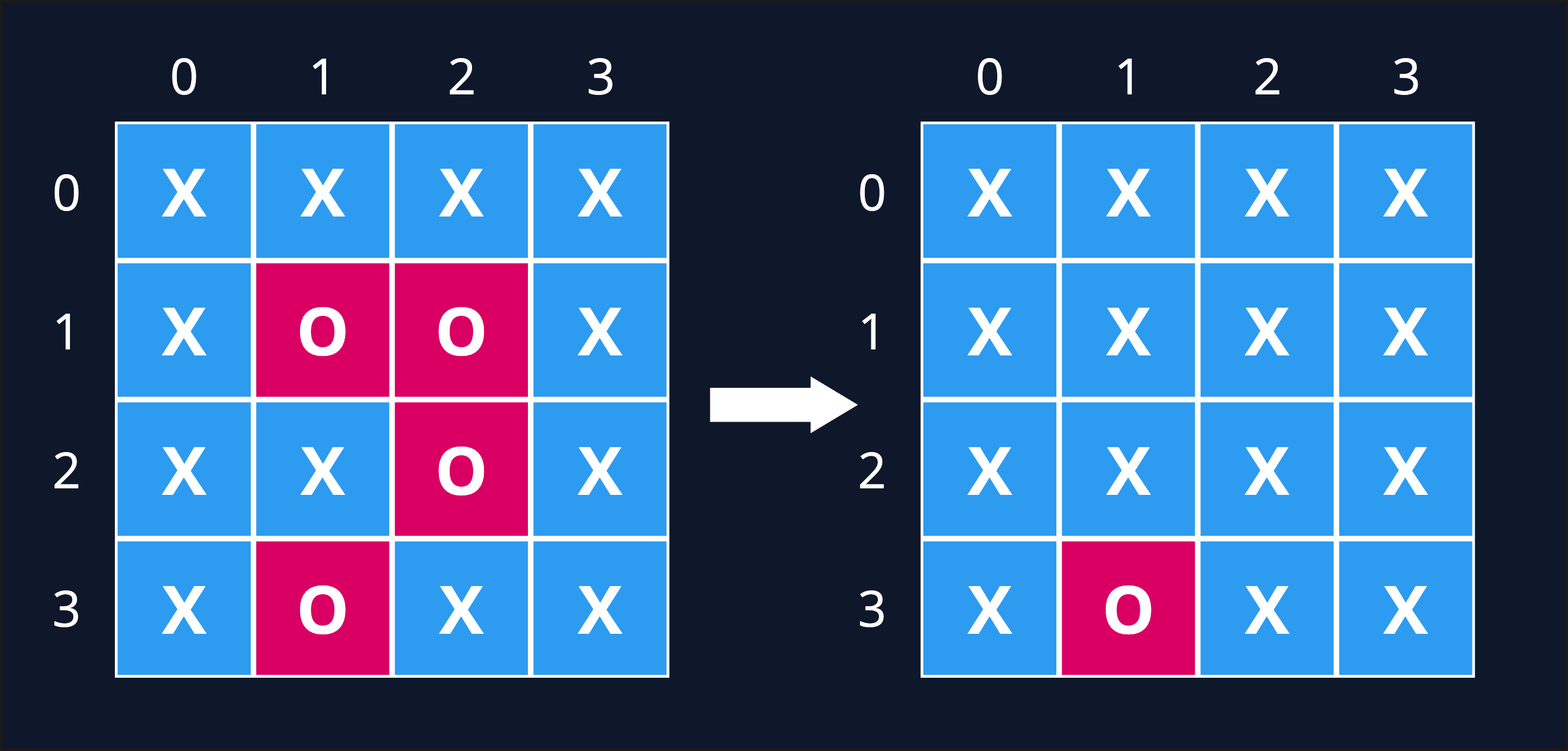
Input: board = [["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","O","X"],["X","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
Output: [["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
Explanation: Notice that an 'O' should not be flipped if:
- It is on the border, or
- It is adjacent to an 'O' that should not be flipped.
The bottom 'O' is on the border, so it is not flipped.
The other three 'O' form a surrounded region, so they are flipped.
Example 2
Input: board = [["X"]]
Output: [["X"]]
Try here before watching the video.
Video Explanation
Java Code
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node {
int row, col;
public Node(int row, int col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
class Solution {
int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}};
private boolean isValidCell(int row, int col, int rows, int cols) {
if(row >= 0 && row < rows && col >= 0 && col < cols)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public void solve(char[][] board) {
int rows = board.length;
int cols = board[0].length;
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(i == 0 || i == rows - 1 || j == 0 || j == cols - 1) {
if(board[i][j] == 'O') {
queue.add(new Node(i, j));
board[i][j] = 'V';
}
}
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
for(int[] direction : directions) {
int newRow = node.row + direction[0];
int newCol = node.col + direction[1];
if(isValidCell(newRow, newCol, rows, cols) && board[newRow][newCol] == 'O') {
queue.add(new Node(newRow, newCol));
board[newRow][newCol] = 'V';
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == 'V') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
}
C++ Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int row, col;
Node(int row, int col) {
this->row = row;
this->col = col;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> directions = {{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}};
bool isValidCell(int row, int col, int rows, int cols) {
if(row >= 0 && row < rows && col >= 0 && col < cols)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void solve(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
int rows = board.size();
int cols = board[0].size();
queue<Node> queue;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(i == 0 || i == rows - 1 || j == 0 || j == cols - 1) {
if(board[i][j] == 'O') {
queue.push(Node(i, j));
board[i][j] = 'V';
}
}
}
}
while(!queue.empty()) {
Node node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
for(auto& direction : directions) {
int newRow = node.row + direction[0];
int newCol = node.col + direction[1];
if(isValidCell(newRow, newCol, rows, cols) && board[newRow][newCol] == 'O') {
queue.push(Node(newRow, newCol));
board[newRow][newCol] = 'V';
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == 'V') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
};
Python Code
from typing import List
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def solve(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> None:
rows, cols = len(board), len(board[0])
distances = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1), (1, 0)]
def is_valid_cell(row, col):
return 0 <= row < rows and 0 <= col < cols
queue = deque()
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if i == 0 or i == rows - 1 or j == 0 or j == cols - 1:
if board[i][j] == 'O':
queue.append((i, j))
board[i][j] = 'V'
while queue:
row, col = queue.popleft()
for direction in distances:
new_row, new_col = row + direction[0], col + direction[1]
if is_valid_cell(new_row, new_col) and board[new_row][new_col] == 'O':
queue.append((new_row, new_col))
board[new_row][new_col] = 'V'
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if board[i][j] == 'V':
board[i][j] = 'O'
elif board[i][j] == 'O':
board[i][j] = 'X'
Javascript Code
class Node {
constructor(row, col) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
var solve = function(board) {
const directions = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0]];
const isValidCell = (row, col, rows, cols) => {
return row >= 0 && row < rows && col >= 0 && col < cols;
};
const rows = board.length;
const cols = board[0].length;
const queue = [];
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (i === 0 || i === rows - 1 || j === 0 || j === cols - 1) {
if (board[i][j] === 'O') {
queue.push(new Node(i, j));
board[i][j] = 'V';
}
}
}
}
while (queue.length > 0) {
const node = queue.shift();
for (const direction of directions) {
const newRow = node.row + direction[0];
const newCol = node.col + direction[1];
if (isValidCell(newRow, newCol, rows, cols) && board[newRow][newCol] === 'O') {
queue.push(new Node(newRow, newCol));
board[newRow][newCol] = 'V';
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (board[i][j] === 'V') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
};
Go Code
type Node struct {
Row int
Col int
}
var directions = [][]int{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}}
func isValidCell(row, col, rows, cols int) bool {
return row >= 0 && row < rows && col >= 0 && col < cols
}
func solve(board [][]byte) {
rows := len(board)
cols := len(board[0])
queue := make([]Node, 0)
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
if i == 0 || i == rows-1 || j == 0 || j == cols-1 {
if board[i][j] == 'O' {
queue = append(queue, Node{i, j})
board[i][j] = 'V'
}
}
}
}
for len(queue) > 0 {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
for _, direction := range directions {
newRow := node.Row + direction[0]
newCol := node.Col + direction[1]
if isValidCell(newRow, newCol, rows, cols) && board[newRow][newCol] == 'O' {
queue = append(queue, Node{newRow, newCol})
board[newRow][newCol] = 'V'
}
}
}
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < cols; j++ {
if board[i][j] == 'V' {
board[i][j] = 'O'
} else {
board[i][j] = 'X'
}
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of cells in the board.
Space Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of cells in the board.