Problem Statement
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
Reorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
You may not modify the values in the list's nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1
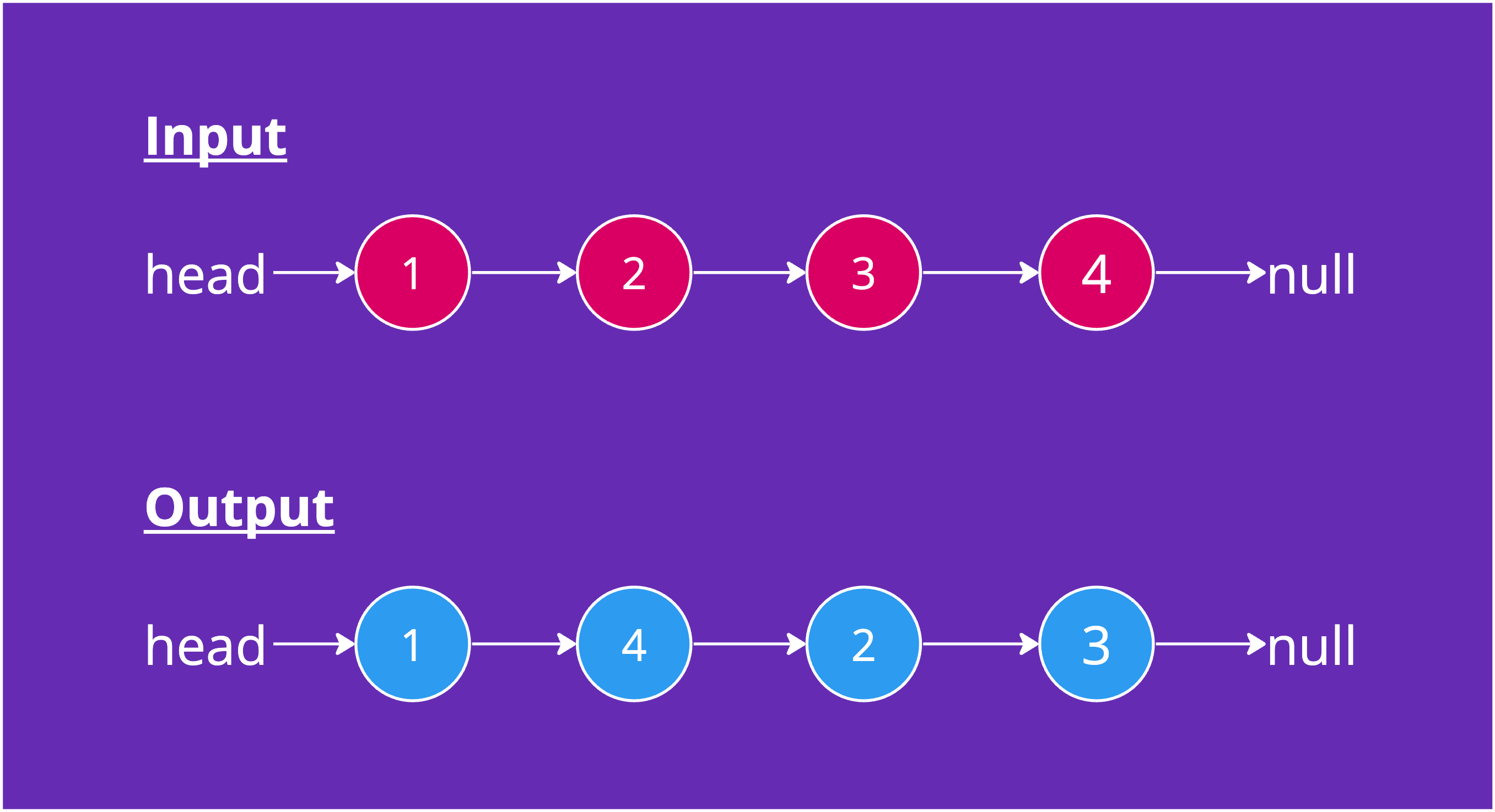
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [1,4,2,3]
Example 2
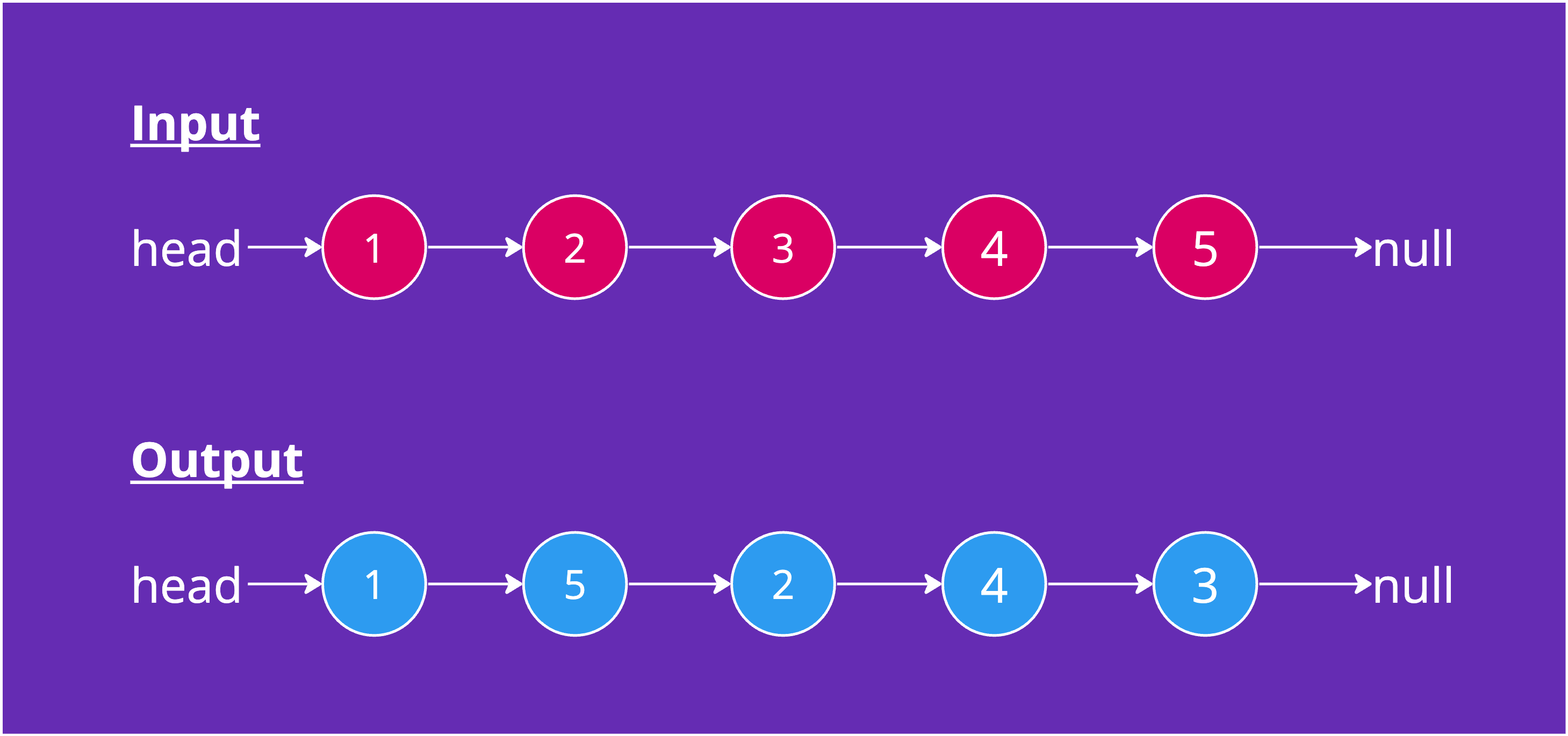
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,5,2,4,3]
Try here before watching the video.
Video Explanation
Java Code
class Solution {
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null, curr = head, next = null;
while(curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
private ListNode findMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow, fast;
slow = fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode mid = findMid(head);
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = reverse(mid);
while(second.next != null) {
ListNode temp = first.next;
first.next = second;
first = temp;
temp = second.next;
second.next = first;
second = temp;
}
}
}
C++ Code
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
ListNode* curr = head;
ListNode* next = nullptr;
while (curr != nullptr) {
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
ListNode* findMid(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* mid = findMid(head);
ListNode* first = head;
ListNode* second = reverse(mid);
while (second->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* temp = first->next;
first->next = second;
first = temp;
temp = second->next;
second->next = first;
second = temp;
}
}
};
Python Code
class Solution:
def reverse(self, head):
prev = None
curr = head
while curr:
next_node = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next_node
return prev
def findMid(self, head):
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
def reorderList(self, head):
mid = self.findMid(head)
first = head
second = self.reverse(mid)
while second.next:
temp = first.next
first.next = second
first = temp
temp = second.next
second.next = first
second = temp
Javascript Code
var reorderList = function(head) {
const reverse = (head) => {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
let next = null;
while (curr !== null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
const findMid = (head) => {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
let mid = findMid(head);
let first = head;
let second = reverse(mid);
while (second.next !== null) {
let temp = first.next;
first.next = second;
first = temp;
temp = second.next;
second.next = first;
second = temp;
}
};
Go Code
func reverse(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
var prev, curr, next *ListNode
curr = head
for curr != nil {
next = curr.Next
curr.Next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
}
return prev
}
func findMid(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
slow, fast := head, head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
return slow
}
func reorderList(head *ListNode) {
mid := findMid(head)
first := head
second := reverse(mid)
for second.Next != nil {
temp := first.Next
first.Next = second
first = temp
temp = second.Next
second.Next = first
second = temp
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N)
1. Firstly, we iterate over the linked list using slow and fast pointers to find the middle node which takes almost N time.
2. Secondly, we are reversing the second half of the linked list which takes almost N time.
3. Then we are rearranging the pointers of the first half and second half which again takes almost N time.
Space Complexity: O(1), in the whole process we're not using any extra space.
